Energy Storage - The Missing Link in Grid Stability
Efficient energy storage systems can be deployed behind-the-meter (BTM) and front-of-the-meter (FTM) to miti- gate the effects of intermittent renewable resources, allowing increased renewable energy utilization and stability of the grid. The mass deployment of energy storage solutions is key to expanding the reach of renewables and speeding the transition to a carbon-free power grid.
September 21, 2021. By News Bureau

A significant percentage of the global energy demand is now met through renewable energy. At 136 GW, which is about 36% of its total installed capacity, India has the 4th largest renewable energy capacity in the world. Setting itself a target of 175 GW of installed renewable energy capacity by 2022, India is growing at the fastest speed among all major countries. However, cycling between oversupply when the sun shines or the wind blows, and shortage when the sun sets or the wind drops, remains the biggest obstacle to renewable energy adoption.
Efficient energy storage systems can be deployed behind-the-meter (BTM) and front-of-the-meter (FTM) to mitigate the effects of intermittent renewable resources, allowing increased renewable energy utilization and stability of the grid. The mass deployment of energy storage solutions is key to expanding the reach of renewables and speeding the transition to a carbon-free power grid. Installation of BTM batteries is already on the rise in India as rooftop solar PV applications. The FTM batteries provide stability to the grid by storing excess energy and frequency rotation (guiding the grid’s electric frequency on a real-time basis) and providing transmission and distribution support to smoothen out the energy flows.

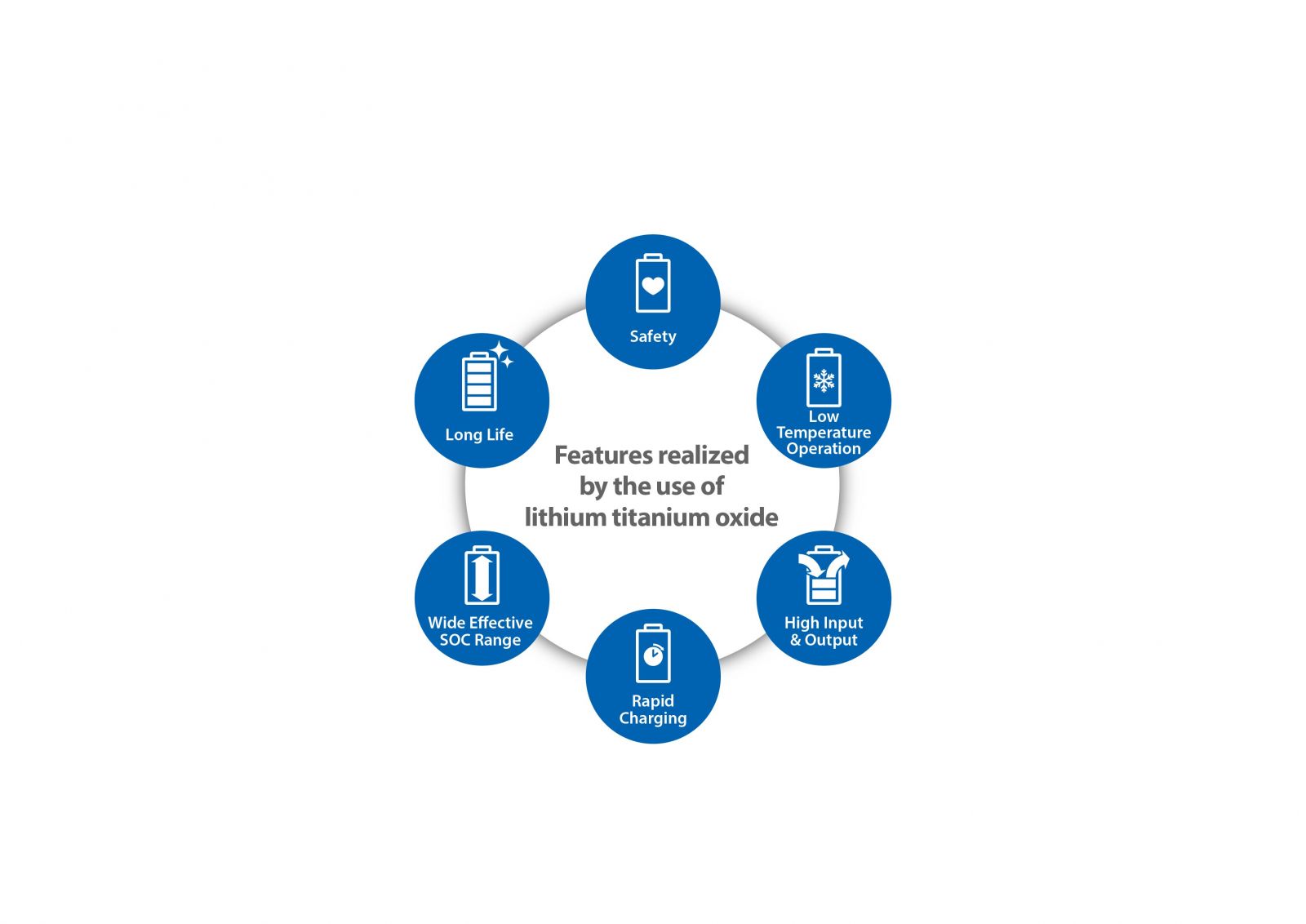
At Toshiba, we always look for better ways of generating and applying clean, sustainable, and reliable energy. Generations of venture spirit and innovation at our core led to the development of Toshiba’s rechargeable battery – SCiBTM. Its six distinguished characteristics make it the most versatile and optimal choice for regular stationary storage (RE storage) and ancillary services application.
With SCiBTM batteries installed as part of the solar energy generation system, DC energy being produced by the solar panels can be stored as AC power for later use when solar panels aren’t producing electricity or if there is a power outage. The flexible stackable capacity of the SCiBTM battery allows it to store more solar energy.

Another distinguishing quality of Toshiba SCiBTM batteries lies in their safety. They have excellent thermal performance, reducing or eliminating the need for battery cooling. The lithium titanate oxide (LTO) chemistry contained in SCiBTM is not susceptible to thermal runaway and can operate at extreme temperatures as low as -30°C, up to 60°C, providing exceptional battery safety characteristics. If a foreign object like a metal gets mixed in between the cathode and anode by mistake, the lithium ions are instantly released from the LTO close to the short circuit point, turning the LTO anode into an insulator (high-resistive phase). This prevents the flow of excessive short circuit currents and controls the battery’s thermal runaway. That’s how the self-protection mechanism works.

SCiBTM products also offer marginal capacity degradation even after more than 20,000 charge-discharge cycles. This operational life often exceeds that of the applications in which they are used, thus greatly reducing the frequency of battery replacement, and reducing the environmental impact of waste batteries.
Toshiba is harnessing its knowledge and expertise to deliver clean energy solutions and will continue to develop innovative solutions to support reliable electric power supply turning on the promise of a new day.
Efficient energy storage systems can be deployed behind-the-meter (BTM) and front-of-the-meter (FTM) to mitigate the effects of intermittent renewable resources, allowing increased renewable energy utilization and stability of the grid. The mass deployment of energy storage solutions is key to expanding the reach of renewables and speeding the transition to a carbon-free power grid. Installation of BTM batteries is already on the rise in India as rooftop solar PV applications. The FTM batteries provide stability to the grid by storing excess energy and frequency rotation (guiding the grid’s electric frequency on a real-time basis) and providing transmission and distribution support to smoothen out the energy flows.

At Toshiba, we always look for better ways of generating and applying clean, sustainable, and reliable energy. Generations of venture spirit and innovation at our core led to the development of Toshiba’s rechargeable battery – SCiBTM. Its six distinguished characteristics make it the most versatile and optimal choice for regular stationary storage (RE storage) and ancillary services application.

With SCiBTM batteries installed as part of the solar energy generation system, DC energy being produced by the solar panels can be stored as AC power for later use when solar panels aren’t producing electricity or if there is a power outage. The flexible stackable capacity of the SCiBTM battery allows it to store more solar energy.

Another distinguishing quality of Toshiba SCiBTM batteries lies in their safety. They have excellent thermal performance, reducing or eliminating the need for battery cooling. The lithium titanate oxide (LTO) chemistry contained in SCiBTM is not susceptible to thermal runaway and can operate at extreme temperatures as low as -30°C, up to 60°C, providing exceptional battery safety characteristics. If a foreign object like a metal gets mixed in between the cathode and anode by mistake, the lithium ions are instantly released from the LTO close to the short circuit point, turning the LTO anode into an insulator (high-resistive phase). This prevents the flow of excessive short circuit currents and controls the battery’s thermal runaway. That’s how the self-protection mechanism works.

SCiBTM products also offer marginal capacity degradation even after more than 20,000 charge-discharge cycles. This operational life often exceeds that of the applications in which they are used, thus greatly reducing the frequency of battery replacement, and reducing the environmental impact of waste batteries.
Toshiba is harnessing its knowledge and expertise to deliver clean energy solutions and will continue to develop innovative solutions to support reliable electric power supply turning on the promise of a new day.
- Tomohiko Okada, Managing Director, Toshiba India Pvt Ltd
If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content,
please contact: contact@energetica-india.net.
please contact: contact@energetica-india.net.

















