(Em)Powering The Future of Energy
As India begins the process of de-carbonising its economy, technologies like CO2 capture, Virtual Power Plant, Hydrogen energy will play a key role in solving its long-term energy challenges, and regulating the ups and downs in supply from renewable sources.
October 26, 2021. By News Bureau

Rapid urbanization and industrialization supplemented by an expanding economy, a growing population, and improving quality of life has created enormous energy demand in India. To achieve a high energy self-sufficiency rate, India still largely depends on thermal-power. But India’s Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) ratified in the Paris Agreement compels the government to encourage alternative energy sources to reduce emissions against GDP by 33-35%, to below 2005 levels, by 2030. There is no doubt that India’s future prosperity will depend on affordable, clean and reliable energy sources that are environmentally friendly.
For over 50 years, Toshiba Group has been India’s strategic partner in the energy sector, providing integrated solutions ranging across power generation, transmission, distribution, storage and management. The company’s global experience, local manufacturing capabilities and emphasis on R&D into technologies that contribute to carbon neutrality, have helped to win an outstanding reputation in the market, and ensure that Toshiba is well positioned to support India’s resolve to achieve its NDC under the Paris Agreement.
“We believe that innovative energy technologies are the key to achieving sustainable growth. Toshiba develops and utilises advanced technology and solutions to create energy systems that sustain our lives, and our planet. To accelerate sustainability through a low-carbon economy, Toshiba Group’s Environmental Future Vision 2050 aims to halve greenhouse gas emissions throughout our value chain by 2030, compared to 2019. In our operations here in India, we look forward to introducing more advanced technologies to support the energy solutions needed in India for a sustainable NEW DAY.” Toshiba’s businesses in India offer technologies and services for generating, transmitting and distributing energy for the realization of a low carbon economy.
Looking to the future and beyond
For over 50 years, Toshiba Group has been India’s strategic partner in the energy sector, providing integrated solutions ranging across power generation, transmission, distribution, storage and management. The company’s global experience, local manufacturing capabilities and emphasis on R&D into technologies that contribute to carbon neutrality, have helped to win an outstanding reputation in the market, and ensure that Toshiba is well positioned to support India’s resolve to achieve its NDC under the Paris Agreement.
“We believe that innovative energy technologies are the key to achieving sustainable growth. Toshiba develops and utilises advanced technology and solutions to create energy systems that sustain our lives, and our planet. To accelerate sustainability through a low-carbon economy, Toshiba Group’s Environmental Future Vision 2050 aims to halve greenhouse gas emissions throughout our value chain by 2030, compared to 2019. In our operations here in India, we look forward to introducing more advanced technologies to support the energy solutions needed in India for a sustainable NEW DAY.” Toshiba’s businesses in India offer technologies and services for generating, transmitting and distributing energy for the realization of a low carbon economy.
Looking to the future and beyond

As India begins the process of de-carbonising its economy, technologies like CO2 capture, Virtual Power Plant, Hydrogen energy will play a key role in solving its long-term energy challenges, and regulating the ups and downs in supply from renewable sources.
• CO2 capture technology: efforts for CO2 emission reduction
Carbon dioxide Capture and Storage (CCS) is a range of technologies to separate, capture, and sequester CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial sector, so that it is not released to the atmosphere to contribute to climate change. CCS is essential for the current transition toward a low-carbon society. Toshiba employs post combustion capture technology based on a chemical absorption process, a technology that can be applied flexibly to various flue gas streams, including but not limited to thermal power plants. The company is now accelerating development and deployment of the technology in the market. In Japan, it has constructed the world’s first commercial use Carbon dioxide capture and utilization (CCU) plant in a municipal waste incineration plant in Saga city in 2016.
• Virtual power plant (VPP): a new solution today, essential power infrastructure tomorrow
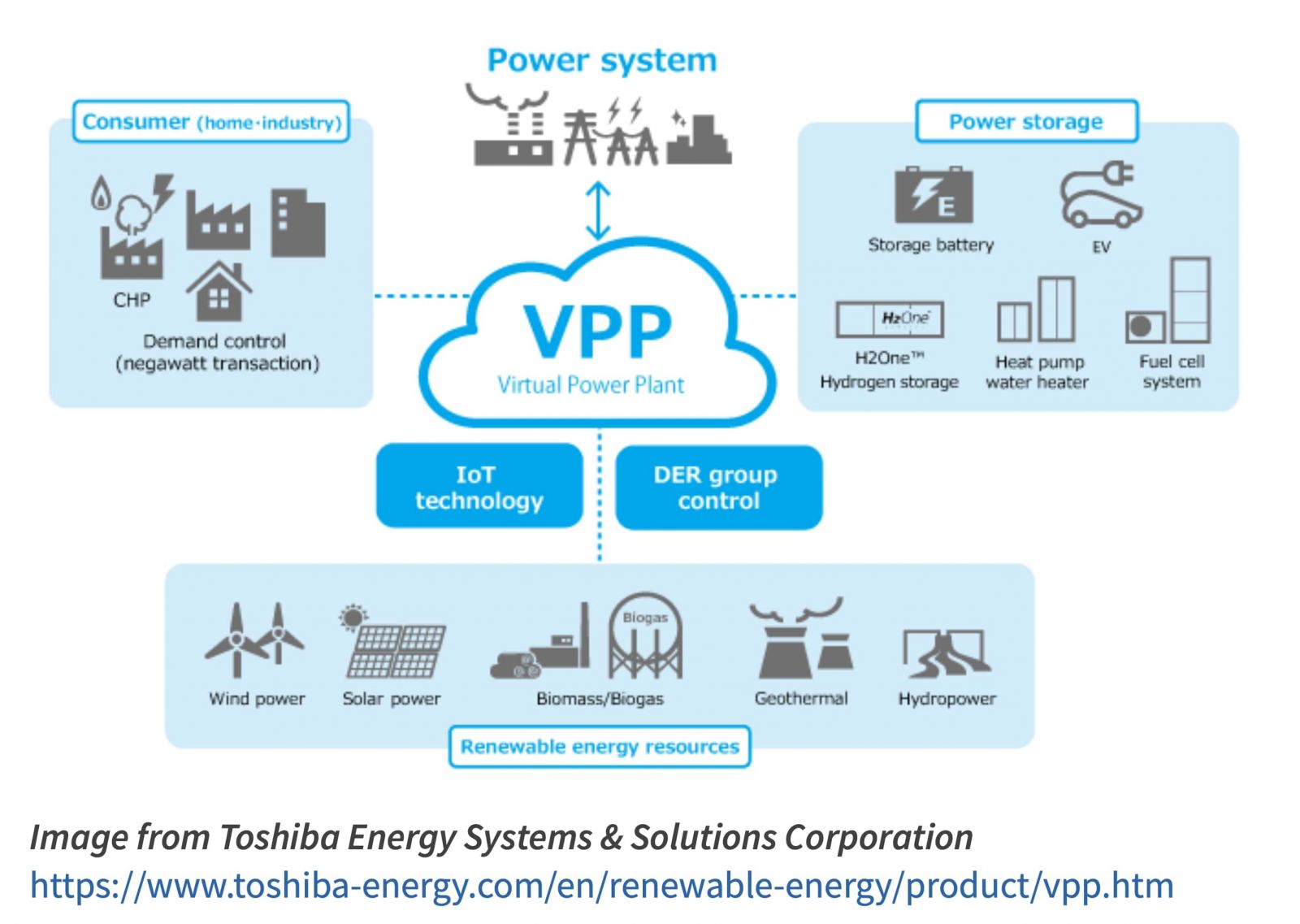
VPP contributes to the optimization of the supply and demand balance in the power network by controlling multiple distributed energy resources effectively, as a single virtual power plant. It can maintain the stability of power supply from renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, which greatly depend on the weather to generate power. VPP is expected to promote the introduction and expansion of renewable energy and contribute to decarbonization.
For example - Toshiba has been operating a demonstration project to develop an intelligent VPP system for storage battery control technology since 2016, and started an optimal control of storage batteries using IoT technology for VPP from January 2019. In 2020, Toshiba set up a joint venture (JV) with Next Kraftwerke GmbH, a German VPP operator, to use VPP technology to provide services that support the balancing mechanism for renewable energy assets owners and aggregators.
Looking to the future, Toshiba is advancing VPP capabilities by integrating AI into forecasting output from renewables, and demand and market prices. The concept of energy service comes as a solution to maintain the stability of the power supply, which means scattered energy sources, such as distributed power sources and storage batteries are remotely controlled by IoT equipment and function.
• Hydrogen energy: from water to water

Hydrogen energy is an important clean energy source. Hydrogen can be stored indefinitely and transported over long distances, and it produces no CO2 when converted to electricity. Any roadmap to a low carbon society recognizes the importance of hydrogen energy, and Toshiba has long devoted resources to developing essential technologies and systems. The company’s first launched hydrogen system is the H2One™ Hydrogen-based Autonomous Energy Supply System.
H2One™ is an integrated system that uses a renewable energy source to electrolyze hydrogen from water, and stores and uses the hydrogen in fuel cells to provide a stable delivery of CO2-free, environmentally-friendly electricity. It can be used even in places where there is no power grid. Its green hydrogen process is CO2 -free throughout the entire cycle of the production, storage, and use, and therefore contributes to curbing global warming.
- Toshiba India
If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content,
please contact: contact@energetica-india.net.
please contact: contact@energetica-india.net.

















